Safety valve gas control pump accessories pressure regulator
Safety valve gas control pump accessories pressure regulator is a key component in the gas supply system. Its main function is to ensure the stable su...
See DetailsNatural gas plays a vital role in modern energy systems, powering residential heating, industrial production, and commercial facilities. To ensure that gas is delivered safely and efficiently, pressure control is one of the most critical aspects of any gas distribution network. This is where a Natural gas pressure regulating box becomes essential.
A Natural gas pressure regulating box is designed to maintain a stable output of gas pressure, preventing sudden fluctuations that could affect the performance of appliances or create safety risks. Without proper regulation, high-pressure gas from the main supply lines could damage pipelines or equipment inside buildings.
In both residential and commercial settings, these regulating systems act as the “safety gatekeepers” of gas flow. They reduce high inlet pressure to a stable, usable level suitable for building distribution. Whether it’s a wall-mounted building pressure regulating box for compact installations or a larger outdoor unit serving multiple connections, the purpose remains the same — to provide steady, safe, and efficient gas delivery.
As buildings become more energy-conscious and regulations tighten, understanding the function and importance of the Natural gas pressure regulating box is more relevant than ever. This article explores how it works, its main types, and why it’s indispensable in modern gas supply systems.
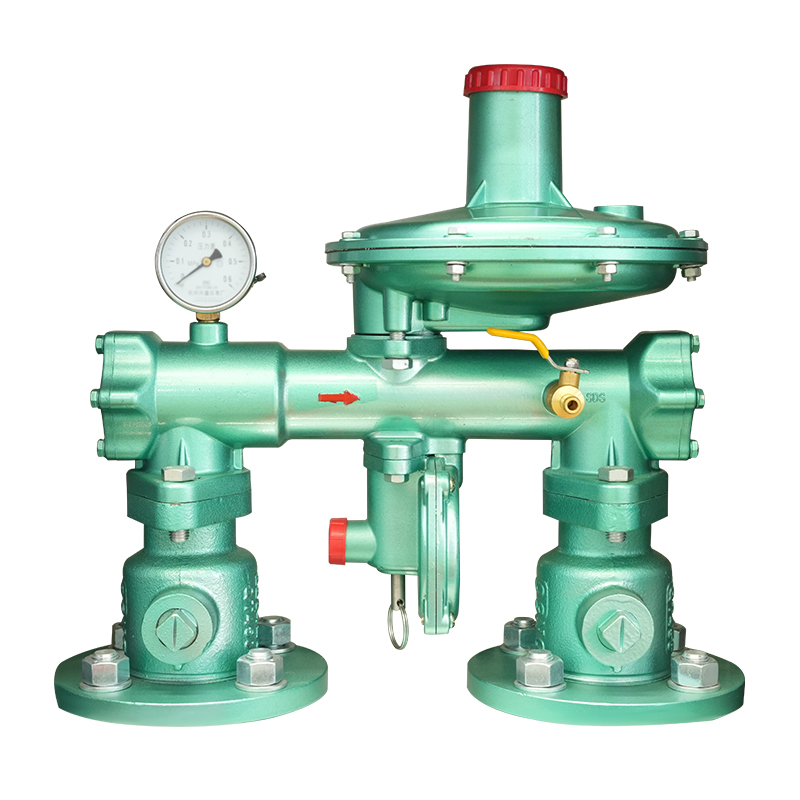
A Natural gas pressure regulating box is a safety and control device used to reduce and stabilize the pressure of gas entering a building or system. It acts as a boundary between the high-pressure gas distribution pipeline and the low-pressure network within the building. Its main function is to regulate gas pressure automatically so that it remains consistent despite fluctuations in supply.
The key components usually include:
These elements are enclosed in a protective box, which can be installed on exterior walls, inside service rooms, or on outdoor platforms depending on the type and capacity of the system.
The wall-mounted building pressure regulating box is designed for compact spaces and residential applications. It is typically installed on exterior walls to simplify piping connections and maintenance access. Its advantages include small size, easy installation, and suitability for medium and low-pressure systems.
Outdoor units are used in industrial or multi-building installations where higher gas flow and pressure control are required. They are usually equipped with more robust regulators and protective enclosures made from corrosion-resistant materials. Such systems can serve entire commercial blocks or manufacturing facilities.
| Type | Installation Location | Pressure Range | Application | Main Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wall-Mounted Building Pressure Regulating Box | Exterior wall or service area | Low to medium | Residential and small commercial buildings | Compact design, easy to maintain, corrosion-protected housing |
| Outdoor Natural Gas Pressure Regulating Box | Outdoor platform or dedicated site | Medium to high | Industrial facilities and large buildings | High capacity, multiple safety features, durable materials |
The working mechanism of a Natural gas pressure regulating box is based on the pressure balance between the inlet (high pressure) and the outlet (low pressure). When gas enters the box, it passes through a regulator that adjusts the flow rate according to the outlet pressure demand.
The entire process is automatic and continuous, ensuring constant pressure despite fluctuations in gas demand or supply.
These boxes are critical components of urban gas networks and ensure safety, efficiency, and compliance with technical standards.
The Natural gas pressure regulating box requires regular maintenance to guarantee reliability and safety. Preventive maintenance detects potential issues such as leaks, corrosion, or wear before they become major hazards. Proper maintenance extends the service life of components and ensures compliance with safety regulations.
| Inspection Interval | Tasks | Applicable Type | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Daily or Weekly | Visual check for gas odor or leaks. Verify pressure gauge readings. Listen for unusual noises or vibrations. | All types | Quick operational checks; record in logbook. |
| Every 3–6 Months | Clean or replace filters. Test safety relief valves. Check tightness of connections. Inspect for corrosion or water ingress. | Outdoor and industrial boxes | May require temporary shutdown. |
| Every 6–12 Months | Calibrate regulator settings. Inspect diaphragm and spring. Test shut-off devices. Check mechanical linkages. | Wall-mounted and medium-pressure systems | Perform during scheduled maintenance periods. |
| Every 2–3 Years | Overhaul or replace regulator. Replace gaskets, seals, sensors. Conduct full leak test under pressure. | All systems | Performed by certified technician. |
| Step | Inspection Item | Purpose | Procedure / Observation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Verify isolation and depressurization | Prevent accidental gas discharge | Close valves, release residual gas, confirm with pressure gauge. |
| 2 | Inspect enclosure integrity | Ensure protection | Check for cracks, corrosion, or loose seals. |
| 3 | Examine piping and joints | Detect leaks | Apply soap solution to joints; observe for bubbles. |
| 4 | Check pressure regulator | Verify outlet stability | Compare inlet/outlet readings during operation. |
| 5 | Test safety devices | Confirm correct operation | Simulate overpressure if safe; check activation threshold. |
| 6 | Review electrical grounding | Prevent static discharge | Measure continuity to ground; ensure bonding. |
| 7 | Restore operation | Return system safely | Open valves slowly, monitor pressure recovery, record readings. |
| Symptom | Possible Cause | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Outlet pressure fluctuates | Diaphragm damage or spring fatigue | Replace diaphragm, recalibrate regulator. |
| Gas odor near enclosure | Leaking joint or deteriorated gasket | Tighten connection, replace sealing components. |
| Slow pressure response | Blocked filter or frozen regulator | Clean or replace filter, add heating. |
| Overpressure at outlet | Relief valve failure or incorrect setpoint | Test and reset valve; replace if defective. |
| Excessive vibration or noise | Gas pulsation or unstable flow | Check flow rate, install dampener. |
Modern Natural gas pressure regulating boxes include sensors for remote monitoring of pressure, temperature, and flow rate. When integrated with Building Management Systems (BMS) or SCADA networks, they enable predictive maintenance. This provides real-time diagnostics, automated alerts, and data-driven decision-making.
Regular inspection and maintenance form the foundation of safe gas operation. The Natural gas pressure regulating box may appear simple, but its precise components require periodic calibration. Consistent maintenance, safety procedures, and smart monitoring ensure continuous gas delivery and system reliability.
The Natural gas pressure regulating box is the silent guardian of every building’s gas supply system. It ensures that natural gas is delivered safely and efficiently. When properly maintained, it forms the foundation of a reliable and energy-efficient gas network.
The Natural gas pressure regulating box combines mechanical precision with built-in safety features. Regular inspection and preventive maintenance are vital to preserving its effectiveness and compliance with standards such as EN 334, NFPA 54, and GB 50028.
A well-calibrated Natural gas pressure regulating box improves energy efficiency and reduces emissions. Stable pressure enables complete combustion, cutting fuel consumption and supporting sustainability goals.
The integration of digital sensors and IoT technologies will make Natural gas pressure regulating boxes part of intelligent monitoring systems. This will transform gas safety management from reactive to predictive.
The Natural gas pressure regulating box represents the intersection of safety, efficiency, and technology. Regular maintenance and quality installation protect lives and enhance system reliability. It remains the heart of modern gas distribution — ensuring our homes, industries, and cities operate safely and efficiently.
A Natural gas pressure regulating box controls and stabilizes gas pressure as it moves from the main supply line into a building or facility. Its role is to reduce high inlet pressure to a safe outlet level, ensuring safe operation and energy efficiency.
Routine inspection should be carried out every 6 to 12 months, depending on conditions and usage. Residential units need annual checks; industrial systems may need inspection every 3–6 months. Tasks include leak checks, calibration, filter cleaning, and safety valve testing.
Contact Us